English: Barbary Sheep; French: Mouflon à manchettes; Arabian: Audan, Aroui el Maghreb; Peulh: Edda; Spanish: Arrui; Tuareg: udad, aoudad.
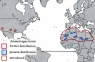
Former distribution: Northern Africa from Mauritania east to the Red Sea.
Present distribution: In restricted areas of northern Mauritania, south-eastern Morocco, central and southern Algeria, southern Libya, north-western Chad, north-western Sudan. Introduced into USA, New Mexico, Texas and California, (1975,1976); Spain, Sierra Espune, and to private farms (1970).
Population status: Extinct in Egypt, rare in Morocco and northern Algeria. Stable in Mauritania, southern Algeria, north-western Chad, and north-western Sudan (Darfur, Ennedi, Tibesti, Fessan, Aïr, Ahaggar, Tassili n’Azdjer, Adrar). Estimated numbers: No records.
Behaviour: Preferred habitat: high desert mountains. Gregarious and associate in small family groups; activity is at twilight; diet includes grasses, herbs, leaves from shrubs and small trees. Predators include leopards and caracals.
Brief notes:
Body weight: 120-140 kg
Head and body length: 155-165 cm
Tail length: 20-25 cm
Shoulder height: 90-100 cm
Gestation period: 150-165 days
Maximum age: 24 years in captivity
Trophy: Record SCI: 140 4/8 score, 1960 Chad, FRANCO MAZZOCCHELLI; 134 6/8 score, 1982 Spain, Dr. M.G. SEQUEIRA. RW’s: 34 5/8, 1947 Chad, Ennedi, F. EDMONDBLANC; average 22″. CIC: 413.10 points, Algeria; average 310 points.
Hunting methods: Stalking, with beaters.
Subspecies: 6, 4 Palaearctic, 2 Afro-tropical region
1. Mauritanian Barbary Sheep Ammotragus l. lervia Morocco and Algeria. Rare.
2. Lybian Barbary Sheep Ammotragus l. fassini Libya. Stable.
3. Egyptian Barbary Sheep Ammotragus l. ornatus Egypt. Extinct.
4. Kordofan Barbary Sheep Ammotragus l. blainei Sudan, Dongola and Kordofan. Stable.
Afro-tropical region
5. Air Barbary Sheep Ammotragus l. angusi Aïr region and Ifoghas. Stable.
6. Sahara Barbary Sheep Ammotragus l. sahariensis Chad, Ahaggar, Tibesti, Tassili n’Azdjer. Stable.
Remarks: During droughts Barbary Sheep sustain heavy losses; a slow decrease due to poaching by natives seems inevitable. Active management and controlled hunting is required in all areas.